ASUS PG27AQDP: Difference between revisions
(Wording) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
=== Color processing noise === | === Color processing noise === | ||
Ideally, the monitor processes incoming pixel values so that the according output luminance follows a smooth transfer function. This processing usually takes place in the digital domain, while aiming for some favorable Gamma characteristic and taking other parameters into account, like the Contrast, the RGB channel gains, and also spatial or spatio-temporal dithering. One way of quantifying how consistently this is done | Ideally, the monitor processes incoming pixel values so that the according output luminance follows a smooth transfer function. This processing usually takes place in the digital domain, while aiming for some favorable Gamma characteristic and while taking other parameters into account, like the Contrast setting, the RGB channel gains, and also spatial or spatio-temporal dithering. One way of quantifying how consistently this is done across the pixel value range, without needing to know the Gamma characteristic specifically targeted, is to measure deviations from a smooth transfer function. This means that we do not focus on how well the transfer function is described by a simple Gamma function, but how well the measured data points can be described by a reasonable smooth transfer function. We only measure the green channel here, because it is the brightest of the color channels normally available and, thereby, provides the best signal-to-noise ratio. Of course, here, where we have also a sub-pixel for white, we could also have measured transfer function for white. The lowest (x<16) and the highest pixel values (x>240) are not taken into account here, for several technical reasons related to the measurement method and data analysis. | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| Line 81: | Line 81: | ||
<xr id="ProcessingNoise" nolink /> shows the results for the ASUS PG27AQDP and, for comparison, the [[BenQ XL2540]]. For this comparison, the ASUS was operated at 8{{unit|bpc}} in order to match the capabilities of the BenQ which accepts only 8{{unit|bpc}} inputs. Clearly, the ASUS is doing much worse in this test than the BenQ (SD=22.3% vs. SD=6.3%; smaller standard deviations are better). | <xr id="ProcessingNoise" nolink /> shows the results for the ASUS PG27AQDP and, for comparison, the [[BenQ XL2540]]. For this comparison, the ASUS was operated at 8{{unit|bpc}} in order to match the capabilities of the BenQ which accepts only 8{{unit|bpc}} inputs. Clearly, the ASUS is doing much worse in this test than the BenQ (SD=22.3% vs. SD=6.3%; smaller standard deviations are better). | ||
This measure should closely correspond to the [https://www.rtings.com/monitor/reviews/asus/rog-swift-oled-pg27aqdp#test_1443 ''Gradient score'' given in the RTings.com review], which is 9.8 of the possible 10.0. Obviously, this is not at all in agreement with our findings and probably the result of RTings.com scoring the gradient subjectively and with a rather poor score resolution. The vast majority of the monitors tested by RTings.com are scoring between 9.5 and 9.9. | This measure should closely correspond to the [https://www.rtings.com/monitor/reviews/asus/rog-swift-oled-pg27aqdp#test_1443 ''Gradient score'' given in the RTings.com review], which is 9.8 of the possible 10.0. Obviously, this is not at all in agreement with our findings and probably the result of RTings.com scoring the gradient subjectively and with a rather poor score resolution. The vast majority of the monitors tested by RTings.com are scoring between 9.5 and 9.9, which is only 5 steps for basically the entire relevant range. | ||
The poor color processing also leaves marks at the very low end of the gamma curve, as | The poor color processing also leaves marks at the very low end of the gamma curve, as shown in <xr id="GammaLowEnd" nolink />, which compares the gamma curve of the BenQ (for the green channel) to the gamma curve for the ASUS (for the white channel). For this comparison, both monitors were adjusted to reach approximately max. 150{{cd_m2}} for the respective channels (green for the BenQ, white of the ASUS). Note that, although the low OLED dark-gray luminances push colorimeters to their limits, the notably large luminance steps shown in <xr id="GammaLowEnd" nolink /> (e.g., at pixel values 15 and 23) are real and were also quite obvious when just looking at the monitor with the naked eye while stepping through the values. | ||
{{clr}} | {{clr}} | ||
Although the ASUS, being an HDR-capable monitor, allows input signals with | Although the ASUS, being an HDR-capable monitor, allows input signals with 10{{unit|bpc}} color depth, this does not make a difference for this test (<xr id="ProcessingNoise10bpc" nolink />). If the results were different at all, we would expect the 10{{unit|bpc}} results to be actually worse than the 8{{unit|bpc}} results, as explained in more detail in the [[Razer_Raptor_27_165Hz#Color_processing_noise|Razer Raptor 27 165Hz]] review. For the ASUS, however, the 8{{unit|bpc}} and 10{{unit|bpc}} results are absolutely identical except for the measurement noise. | ||
{{clr}} | {{clr}} | ||
<figure id="ProcessingNoise10bpc" noblock> | <figure id="ProcessingNoise10bpc" noblock> | ||
| Line 95: | Line 95: | ||
The following measurements were made with a {{pda36}}, the gain of which was set to 60{{unit|dB}} resulting in a bandwidth of 37.5{{unit|kHz}} and a minimal rise/fall time (10%-90%) of about 9{{unit|µs}}. The photodiode was placed at 4.5{{unit|cm}} from the screen surface at a straight angle. Ambient light was kept from the measured area by a rubber sleeve of 3{{unit|cm}} diameter which also limited the maximal incident angle to about ±20°. | The following measurements were made with a {{pda36}}, the gain of which was set to 60{{unit|dB}} resulting in a bandwidth of 37.5{{unit|kHz}} and a minimal rise/fall time (10%-90%) of about 9{{unit|µs}}. The photodiode was placed at 4.5{{unit|cm}} from the screen surface at a straight angle. Ambient light was kept from the measured area by a rubber sleeve of 3{{unit|cm}} diameter which also limited the maximal incident angle to about ±20°. | ||
The vertical extent of the measured screen area was not only limited by the rubber sleeve but also by the stimulus being a horizontal stripe covering just 5% of the screen height. Note that the OLED pixels are updated sequentially from the top of the screen to the bottom, which results in different delays for the luminance curves, depending on the vertical measurement position. By limiting the measurement to only 5% of the full vertical screen size, the smear effect caused by averaging over differently delayed luminance signals is limited to a | The vertical extent of the measured screen area was not only limited by the rubber sleeve but also by the stimulus being a horizontal stripe covering just 5% of the screen height. Note that the OLED pixels are updated sequentially from the top of the screen to the bottom, which results in different delays for the luminance curves, depending on the vertical measurement position. By limiting the measurement to only 5% of the full vertical screen size, the smear effect caused by averaging over differently delayed luminance signals is limited to a well defined value. For example, at a refresh frequency of 120{{unit|Hz}}, the screen is updated within around 8{{unit|ms}}, so that a theoretically instant luminance onset on a single-pixel level would result in a measured luminance curve with a 0% to 100% transition ramp over a duration of 5%·8{{unit|ms}} = 0.4{{unit|ms}}. This smear effect is what limits the bandwidth of the measurement and determines, for example, the shortest rise/fall times that can be accurately measured this way. Normally, i.e., when measuring LCDs, this is not the overall-limiting factor, because LCD pixels switch considerably slower anyway. But with OLEDs, where the luminance onset – on the single-pixel level – can indeed be assumed to be instantaneous, this smear effect is the overall-limiting factor.<br/> | ||
For more detailed information on the measurement method and the presentation of the results, see [[Flicker-free settling]]. | For more detailed information on the measurement method and the presentation of the results, see [[Flicker-free settling]]. | ||
==== Settling curves ==== | ==== Settling curves ==== | ||
<xr id="Settling_120_240" nolink /> shows the luminance signal over time for the horizontal stripe being switched from black to white and back. Since the pixels in OLED monitors respond virtually instantaneously, the exact shape of the luminance transition is of minor interest. Nevertheless, <xr id="Settling_120_240" nolink /> still provides some noteworthy | <xr id="Settling_120_240" nolink /> shows the luminance signal over time for the horizontal stripe being switched from black to white and back. Since the pixels in OLED monitors respond virtually instantaneously, the exact shape of the luminance transition is of minor interest. Nevertheless, <xr id="Settling_120_240" nolink /> still provides some noteworthy insights. | ||
# The latency (or input lag) is as short as can be expected, namely about half the duration of a refresh cycle. Note that these measurements were taken at the vertical screen center; therefore, and assuming that the pixels are updated right at the time they are received from the PC, half of the frame data had to be received when the update process arrives at the vertical screen center where the photodiode was placed at, which explains the measured latency of half a refresh frame cycle. | # The latency (or input lag) is as short as can be expected, namely about half the duration of a refresh cycle. Note that these measurements were taken at the vertical screen center; therefore, and assuming that the pixels are updated right at the time they are received from the PC, half of the frame data had to be received when the update process arrives at the vertical screen center where the photodiode was placed at, which explains the measured latency of half a refresh frame cycle. | ||
# The amplitude for the first refresh cycle is higher than for later refresh cycles, as if the monitor was using overdrive. This is only the case for specific luminance values though, which | # The amplitude for the first refresh cycle after the switch is higher than for later refresh cycles, as if the monitor was using overdrive. This is only the case for specific luminance values though, which will be shown in the [[#Settling_matrix_measurements|''Settling matrix measurements'']] section. | ||
# Each refresh cycle ends (or | # Each refresh cycle ends (or – depending on how you look at it – starts) with a very brief low pulse. This is typical for OLED monitors and reflects the pixel reset phase that is part of the pixel refresh procedure. We cannot infer any precise per-pixel pulse timing from our simple measurements here, because the photodiode lumps together several pixel lines into one signal, thereby smearing out such short time events, as explained above. But the smearing is why the relative pulse amplitude is seemingly higher for 240{{unit|Hz}} than for 120{{unit|Hz}}; at double the refresh rate, the recorded pixel lines are simply updated twice as fast, which results in less smearing and, thus, in a less ''washed-out'' pulse. | ||
{{clr}} | {{clr}} | ||
<figure id="Settling_120_240" noblock> | <figure id="Settling_120_240" noblock> | ||
[[File:ASUS_PG27AQDP_SettlingCurves_120+240Hz.png|link={{filepath:ASUS_PG27AQDP_SettlingCurves_120+240Hz.png}}|center|thumb|890px|<caption>ASUS PG27AQDP settling curves for switching from black to white and back, at refresh rates of 120{{unit|Hz}} (left) and 240{{unit|Hz}} (right).<br/> | [[File:ASUS_PG27AQDP_SettlingCurves_120+240Hz.png|link={{filepath:ASUS_PG27AQDP_SettlingCurves_120+240Hz.png}}|center|thumb|890px|<caption>ASUS PG27AQDP settling curves for switching from black to white and back, at refresh rates of 120{{unit|Hz}} (left) and 240{{unit|Hz}} (right).<br/> | ||
The vertical gray lines mark the times when the OpenGL command sequence ''SwapBuffers();glFinish();'' returns control to the PC program, which is about when the 1st line of a frame is sent out to the monitor. This is also when, for the black to white frame switch, a hardware trigger is updated (pink trace), which is recorded along with the photodiode signal. | The vertical gray lines mark the times when the OpenGL command sequence ''SwapBuffers();glFinish();'' returns control to the PC program, which is about when the 1st line of a frame is sent out to the monitor. This is also when, for the black to white frame switch, a hardware trigger is updated (pink trace), which is recorded along with the photodiode signal. For this recording, the photodiode was placed at the vertical center of the screen.</caption>]] | ||
</figure> | </figure> | ||
Revision as of 14:21, 15 January 2025

Specifications
| Brand: | ASUS |
|---|---|
| Model: | ROG Swift PG27AQDP |
| Size: | 26.5" |
| Resolution: | 2560x1440 |
| Panel type: | WOLED |
| Max. refresh rate: | 480 Hz |
| Panel: | ? (LG) |
| Backlight type: | n/a |
| Price (approx.): | USD 1000 |
| Monitor release date: | 2024-08 |
| This review's date: | 2024-12 |
Other Reviews
TFTcentral review of the ASUS ROG Swift PG27AQDP.
RTings.com review of the ASUS ROG Swift PG27AQDP.
At a glance
This monitor is the first OLED monitor reviewed for this website. Obviously, given that it is OLED, it is light-years ahead of TN and IPS monitors regarding pixel response timing. Also image quality is outstanding and one can only hope that it stays this way as the monitor ages, because OLED technology still comes with the risk of burn-in. To reduce this risk, the monitor will only be tested and later used in the SDR mode (Standard Dynamic luminance Range) and with the "Uniform Brightness" setting enabled, even though the monitor supports HDR (High Dynamic luminance Range). Moreover, we intend to use the monitor only at max. 100 cd/m2 and without BFI (Black Frame Insertion), all of which should help extending the monitor's usable lifetime. Nevertheless, BFI is still a very welcome option for improving motion clarity, but it requires to push the maximum luminance limit harder than without BFI. The monitor supports BFI with input signals of 120 Hz and 240 Hz, which – in the 240 Hz case – is where the 480 Hz maximum refresh frequency is put to a use without requiring a PC or graphics card that is capable of reliably driving 480 Hz at a 2K pixel resolution. Otherwise, the high temporal resolution can only be used when making sacrifices elsewhere, like spatial pixel resolution, color depth, and/or signal compression level.
Unfortunately, the BFI timing is flawed (see below), but ASUS has been made aware of the issue and might fix it with some future firmware update.
This monitor comes with a WOLED panel, also meaning that it has four sub-pixels per pixel, the normal primary colors (red, green, blue) plus white. The sub-pixels are arranged side-by-side in an RGWB layout, which allows for clearer text rendering than the older RWBG layout. When rendering B/W content (i.e., gray levels), the monitor uses the white sub-pixels almost exclusively, which is interesting especially for applications in vision research, because there is no color-fringing whatsoever. However, this additional sub-pixel makes color calibration more tricky, for the manufacturers and for the users. And, indeed, when it comes to color accuracy, at least when going by the numbers, this monitor performs rather poorly, not only in comparison to IPS monitors but also in comparison to the QD-OLED monitor MSI MPG 271QRX.
Also color processing is not the strong suit of this monitor – to say the least. The gamma transfer functions are exceptionally rough and are often clipped at their upper ends. Moreover, there are no color settings that would allow the user to make adjustments regarding the white sub-pixel. Poor color processing doesn't help with color accuracy, obviously, and color accuracy is indeed rather low. However, this is likely more an effect of the white sub-pixel rather than the poor color processing.
More a matter of personal preference is the anti-glare coating and, possibly in combination, the impact of the sub-pixel layout on, for example, text clarity. The ASUS PG27AQDP has a semi-glossy AG coating, which is very moderate in comparison to the matte AG coatings of other monitors. More AG coating comes with more back-scatter of ambient light, which has a much higher impact on OLED monitors than on, for example, IPS monitors. This is because IPS monitors don't have really deep blacks to begin with, due to their always active backlight, whereas OLED monitors do. How beneficial AG coating is, and how detrimental its effects, obviously depends on the lighting conditions under which the monitor is used. Independent of the lighting conditions is another potential downside of AG coating though, namely its blurring effect, which might make image content appear less crispy. That alone can dominate the over-all impression one might have of the image quality, possibly also irrespective of some particular sub-pixel layout. When it comes to text clarity specifically, even more aspects come into play, like text size, observation distance, pixel density, text foreground and background colors, eyesight, and what not.
What turned out to be not an issue – subjectively, of course – are the large gaps, horizontally and vertically, between the white sub-pixels, which was expected to result in a screen-door effect when looking at B/W content. The blurring effect of the AG coating, even though not perceived as such, might alleviate the potential screen-door effect, and the relatively high pixel resolution does the rest. Also, text clarity is better than anticipated, although it is indeed worse than with an IPS monitor of the same size and pixel resolution. Obviously, higher pixel densities help alleviating the potential downsides specific sub-pixel layouts might have.
Design issues
- The monitor controls, consisting of a 4-way mini joystick with two additional push buttons at its left and right side, are located behind the bezel, at the bottom of the screen and centered horizontally. Although this makes the controls accessible to left- and right-handers equally well – or less well accessible to right-handers when compared to controls located at the right side of the screen –, the push buttons get easily pressed just accidentally while operating the joystick. One will quickly learn how to avoid this, because one of these buttons powers the monitor off. Moreover, the DisplayPort cable runs nearby and might get in the way – more so for right-handers.
- The monitor's back cover is made of a semi-transparent material which, besides looking awkward, results in very bad readability of the port markings.
- The on-screen menu navigation needs some getting used to. For example, returning from a setting to the menu might require a joystick press for some settings, whereas it is just going "left" for other settings.
Firmware
The monitor arrived with firmware version MCM101, which was updated almost immediately to version MCM102 for this review. With the old version, the gamma transfer functions were all over the place, like being clipped at the high end and possibly not even being monotonic. This has improved with the MCM102 version, at least for the Racing mode. Updating the firmware is a matter of putting a file an a USB stick which is then plugged into the monitor, pressing the menu button for 5 seconds, and waiting like 15-20 minutes for the update to finish – unfortunately without getting any visual feedback about the progress while updating. There are reports of weird monitor behavior after having updated the firmware, which might not necessarily be attributed to a crappy new firmware version. Instead, there is perhaps something wrong with the update process itself. Therefore, it is possibly a good idea, as a precaution, to give the monitor a thorough reset (via the monitor's on-screen setting menu) before(!) and after updating the firmware, disconnecting cables that are not needed for the update, and choosing a 60Hz refresh rate before updating.
On the one hand, being able to update the firmware is welcome; on the other hand, this encourages manufacturers to release unfinished products and to make users beta testers. So, it is a double-edged sword.
It is currently unknown how to make the service menu available for this monitor.
OLED care
OLED monitors are potentially susceptible to burn-in, meaning that static image content can alter pixel performance permanently when presented for a prolonged period of time. Manufacturers implement a number of counter-measures, but, luckily – in the case of the ASUS PG27AQDP –, all of these can be switched off in the on-screen settings menu. Another counter-measure is to not present bright image content, where "bright" is relative to the maximum luminance in HDR mode, which is around 450 cd/m2. Time will have to tell whether burn-in is still an issue when operating the monitor under more moderate conditions.
One of the counter-measures implemented by ASUS is called "Screen move". If activated, the entire screen content will be shifted from time to time. Besides "Off", there are three "Screen move" options available: "Slow", "Normal", and "Fast". Contrary to what these names suggest, the motion speed is always one pixel per minute, that is, the screen content is shifted once per minute and by one pixel each time. The options differ in how far the single motion steps can accumulate along X and Y before the motion direction is reversed. In "Slow" mode, this is 3x3 pixels, in "Normal" mode it is 9x9 pixels (see Figure 1), and in "Fast" mode it is 17x17 pixels. The "motion" is not random but follows a figure-of-eight pattern with strictly horizontal and vertical segments, as can be inferred from Figure 1.
Motion blur reduction
Motion blur reduction, which is called ELMB in the monitor settings (Extreme Low Motion Blur), is available only for 120 and 240 Hz refresh rates and is implemented through BFI (Black Frame Insertion). The BFI on/off ratio is fixed to 50:50 for both of these refresh rates. Neither VRR (Variable Refresh Rate) nor HDR (High Dynamic Range) are available while ELMB mode is active. Unfortunately, the monitor does not synchronize all that well to the input signal when ELMB mode is active. It is not that there are visible tearing artifacts, but the monitor skips or repeats frames for adapting its internal average refresh frequency to that of the input signal received from the PC. Moreover – and possibly more severely – the latency of the displayed image with respect to the input signal varies over time. The difference between the shortest and the longest possible latency for, say, the top-leftmost pixel, is one input frame cycle. How often frames are skipped or repeated and how fast the input lag is changing over time depends on how well the monitor's internal refresh rate happens to match the input refresh rate, but the respective cycle time can easily be in the order of minutes, i.e., rather long. Therefore, this is not necessarily a deal-breaker.
By the way, at least with firmware version MCM102, ELMB gets automatically deactivated when (re-)booting the PC. This is likely due to the refresh rate falling back to 60 Hz temporarily during the boot process, thereby causing ELMB, which is not available for 60 Hz, to be deactivated.
Saturation, White

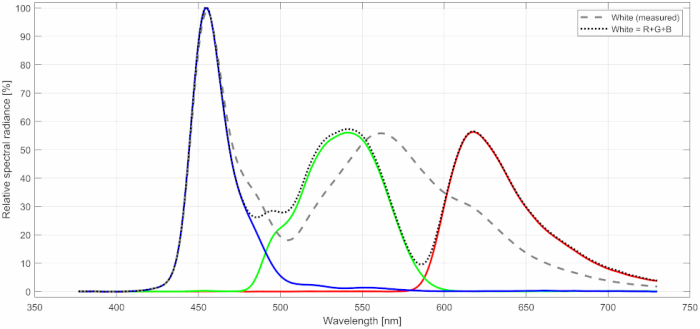
When it comes to color accuracy, one potential problem lies in the interactions between the primary color channels (red, green, blue) when rendering arbitrary colors, including white. Specifically for white, if everything was perfectly accurate, the luminances of the primary colors would add up to LW=LR+LG+LB(=LRGB for short). Ignore, for a moment, that white has its own sub-pixel in this monitor. Deviations from this perfect relationship can be quantified by the (normalized) error Δe=(LRGB−LW) / LRGB (see Figure 2). We can interpret this error also as saturation error, de-saturation, or cross-talk coefficient. Note that, normally, the according measurements are also sensitive to de-saturation effects caused by the residual background illumination, which become overly dominant for dark shades. Besides dark shades being more difficult to measure accurately, this is why dark shades have been excluded from the graphs shown in Figure 2. Obviously, residual background illumination is not an issue with OLED monitors, because they don't have a backlight that would result in residual background illumination. Moreover, because this monitor has a WOLED panel, that is, extra sub-pixels for white, this test does not measure what it was designed to measure in the first place, namely interaction effects between the primary color channels when they are mixed to reproduce white. Still, a big Δe would indicate some sort of color accuracy issue, no matter where the big Δe comes from. The effects would be rather subtle though. For example, unlike with non-WOLED monitors, a big Δe would not mean that all colors appear washed out; it would rather mean that there are some color space distortions somewhere "deeper inside" the color gamut (loosely speaking).
Normally, the Δe somewhat correlates with the more familiar dE color accuracy value known from other review websites. And, indeed, the dE2000-value for this monitor is, with dE2000 = 0.641 (averaged over 400 colors), rather high as compared to 0.152 (Razer), 0.182 (MSI), and 0.428 (BenQ). Note that the white sub-pixel is not only making things more complicated on the monitor side but also on the color measurement side. Colorimeters often can be calibrated for the specific color spectra of the monitor at hand, which works best if there are only 3 color channels to account for. Accounting for a fourth color channel, as for white here, requires compromises to be made in the calibration. It is not clear yet what quantitative impact this has on dE2000 measurements.
Anyway, assuming that these measurements indeed indicate that QD-OLED monitors are better than WOLED monitors in terms of color accuracy, this would be in line with the widespread opinion that QD-LED monitors provide better colors than WOLED monitors. However, what might be meant by "better colors" is not necessarily "better color accuracy" but, rather, more saturated colors. Indeed, QD-OLED colors might be more saturated, especially when it comes to red, but this does not mean that color saturation in WOLED monitors is in any way bad.
Color processing noise
Ideally, the monitor processes incoming pixel values so that the according output luminance follows a smooth transfer function. This processing usually takes place in the digital domain, while aiming for some favorable Gamma characteristic and while taking other parameters into account, like the Contrast setting, the RGB channel gains, and also spatial or spatio-temporal dithering. One way of quantifying how consistently this is done across the pixel value range, without needing to know the Gamma characteristic specifically targeted, is to measure deviations from a smooth transfer function. This means that we do not focus on how well the transfer function is described by a simple Gamma function, but how well the measured data points can be described by a reasonable smooth transfer function. We only measure the green channel here, because it is the brightest of the color channels normally available and, thereby, provides the best signal-to-noise ratio. Of course, here, where we have also a sub-pixel for white, we could also have measured transfer function for white. The lowest (x<16) and the highest pixel values (x>240) are not taken into account here, for several technical reasons related to the measurement method and data analysis.


Figure 3 shows the results for the ASUS PG27AQDP and, for comparison, the BenQ XL2540. For this comparison, the ASUS was operated at 8 bpc in order to match the capabilities of the BenQ which accepts only 8 bpc inputs. Clearly, the ASUS is doing much worse in this test than the BenQ (SD=22.3% vs. SD=6.3%; smaller standard deviations are better).
This measure should closely correspond to the Gradient score given in the RTings.com review, which is 9.8 of the possible 10.0. Obviously, this is not at all in agreement with our findings and probably the result of RTings.com scoring the gradient subjectively and with a rather poor score resolution. The vast majority of the monitors tested by RTings.com are scoring between 9.5 and 9.9, which is only 5 steps for basically the entire relevant range.
The poor color processing also leaves marks at the very low end of the gamma curve, as shown in Figure 4, which compares the gamma curve of the BenQ (for the green channel) to the gamma curve for the ASUS (for the white channel). For this comparison, both monitors were adjusted to reach approximately max. 150 cd/m2 for the respective channels (green for the BenQ, white of the ASUS). Note that, although the low OLED dark-gray luminances push colorimeters to their limits, the notably large luminance steps shown in Figure 4 (e.g., at pixel values 15 and 23) are real and were also quite obvious when just looking at the monitor with the naked eye while stepping through the values.
Although the ASUS, being an HDR-capable monitor, allows input signals with 10 bpc color depth, this does not make a difference for this test (Figure 5). If the results were different at all, we would expect the 10 bpc results to be actually worse than the 8 bpc results, as explained in more detail in the Razer Raptor 27 165Hz review. For the ASUS, however, the 8 bpc and 10 bpc results are absolutely identical except for the measurement noise.
Settling behavior
The following measurements were made with a photo diode PDA36A (Thorlabs), the gain of which was set to 60 dB resulting in a bandwidth of 37.5 kHz and a minimal rise/fall time (10%-90%) of about 9 µs. The photodiode was placed at 4.5 cm from the screen surface at a straight angle. Ambient light was kept from the measured area by a rubber sleeve of 3 cm diameter which also limited the maximal incident angle to about ±20°.
The vertical extent of the measured screen area was not only limited by the rubber sleeve but also by the stimulus being a horizontal stripe covering just 5% of the screen height. Note that the OLED pixels are updated sequentially from the top of the screen to the bottom, which results in different delays for the luminance curves, depending on the vertical measurement position. By limiting the measurement to only 5% of the full vertical screen size, the smear effect caused by averaging over differently delayed luminance signals is limited to a well defined value. For example, at a refresh frequency of 120 Hz, the screen is updated within around 8 ms, so that a theoretically instant luminance onset on a single-pixel level would result in a measured luminance curve with a 0% to 100% transition ramp over a duration of 5%·8 ms = 0.4 ms. This smear effect is what limits the bandwidth of the measurement and determines, for example, the shortest rise/fall times that can be accurately measured this way. Normally, i.e., when measuring LCDs, this is not the overall-limiting factor, because LCD pixels switch considerably slower anyway. But with OLEDs, where the luminance onset – on the single-pixel level – can indeed be assumed to be instantaneous, this smear effect is the overall-limiting factor.
For more detailed information on the measurement method and the presentation of the results, see Flicker-free settling.
Settling curves
Figure 6 shows the luminance signal over time for the horizontal stripe being switched from black to white and back. Since the pixels in OLED monitors respond virtually instantaneously, the exact shape of the luminance transition is of minor interest. Nevertheless, Figure 6 still provides some noteworthy insights.
- The latency (or input lag) is as short as can be expected, namely about half the duration of a refresh cycle. Note that these measurements were taken at the vertical screen center; therefore, and assuming that the pixels are updated right at the time they are received from the PC, half of the frame data had to be received when the update process arrives at the vertical screen center where the photodiode was placed at, which explains the measured latency of half a refresh frame cycle.
- The amplitude for the first refresh cycle after the switch is higher than for later refresh cycles, as if the monitor was using overdrive. This is only the case for specific luminance values though, which will be shown in the Settling matrix measurements section.
- Each refresh cycle ends (or – depending on how you look at it – starts) with a very brief low pulse. This is typical for OLED monitors and reflects the pixel reset phase that is part of the pixel refresh procedure. We cannot infer any precise per-pixel pulse timing from our simple measurements here, because the photodiode lumps together several pixel lines into one signal, thereby smearing out such short time events, as explained above. But the smearing is why the relative pulse amplitude is seemingly higher for 240 Hz than for 120 Hz; at double the refresh rate, the recorded pixel lines are simply updated twice as fast, which results in less smearing and, thus, in a less washed-out pulse.
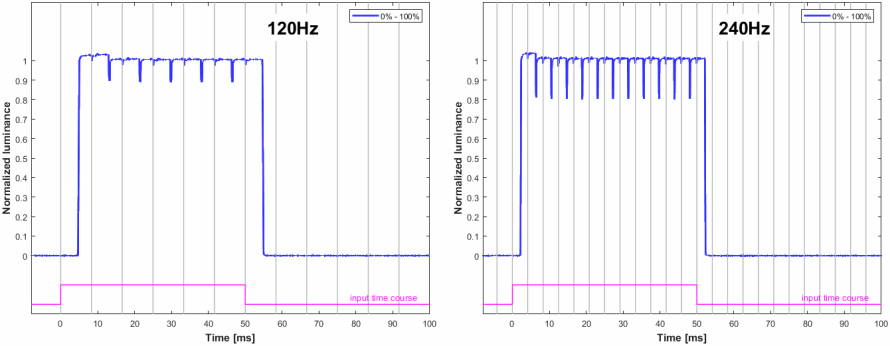
The vertical gray lines mark the times when the OpenGL command sequence SwapBuffers();glFinish(); returns control to the PC program, which is about when the 1st line of a frame is sent out to the monitor. This is also when, for the black to white frame switch, a hardware trigger is updated (pink trace), which is recorded along with the photodiode signal. For this recording, the photodiode was placed at the vertical center of the screen.
Settling matrix measurements
The metrics typically presented in this section, such as settling times, fall/rise times, and similar measures, are intended to characterize the shape of the pixel response curves. However, for OLED monitors with their ultra-fast pixel response times, most of these measures have become largely irrelevant. Those that remain useful may need to be redefined to account for new signal features, such as the reset pulse, to ensure the measures are not contaminated by such features.
Figure 6, in particular, suggests that overshoot – or, alternatively, the average luminance error in the first refresh cycle after a pixel level change – might be worth looking at. Since luminance remains mostly constant throughout a refresh cycle, the average luminance error appears to be the more appropriate measure here, provided that sample time points potentially affected by the limitations of the measurement method are excluded. This also means that the pixel reset pulse is excluded from averaging.

The z-axis for the MSI matrix plots has been clipped at 6% to improve the scale for the values of interest. Note the different z-axis scales for the two monitors.
A "positive" error corresponds to the luminance being higher in the first refresh cycle than in later refresh cycles, no matter whether the FROM pixel value was larger or smaller than the TO pixel value.
To assess the aforementioned luminance error, the methods described in Flicker-free settling were used, with some modifications: the photodiode gain was set to 60 dB (instead of 70 dB), a low-pass filter frequency of 4 kHz (instead of 70 Hz) was applied to preserve the features of the fast OLED pixel response, and signal averaging was limited to an interval that is free of potentially contaminated samples, as outlined above. Note that, with these procedural adjustments, the signal bandwidth is ultimately constrained by the width of the measured stripe on the screen.
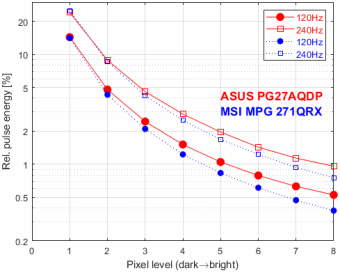
Figure 7 shows the luminance errors for the first refresh cycle after a pixel level change, for 120 Hz and 240 Hz, compared against the MSI MPG 271QRX. The large negative errors for the MSI are mainly caused by a slow rise time rather than by reaching a too low luminance in the first refresh cycle. In direct comparison to the ASUS, the MSI exhibits smaller errors for low-to-high pixel level changes (FROM < TO) but larger errors for high-to-low pixel level changes (FROM > TO). Even though ASUS exhibits errors up to 5%, and only when switch from black to anything brighter, these values are still way smaller than for LCD monitors, where anything below 20% would be considered above-average good already. Whether a 5% error holds any practical relevance or not, the observed error pattern raises questions about the underlying causes.
Could it be that the measured luminance deviations are actually not errors but compensations for, e.g., detrimental effects of the pixel reset pulse, similar to how overdrive in LCD monitors accelerates (and compensates for) slow rise and fall times? On the one hand, the reset pulse – on a single pixel level, i.e., not as measured here – is considered to be too short to have any relevant effect on the luminous output energy per refresh cycle; on the other hand, these pulses obviously carry enough energy to leave traces in our bandwidth-limited signal (see Figure 6). Note that the reset pulse is always negative, thereby giving high-to-low pixel level switches a slight advantage, regarding switching latency, over low-to-high switches, at least for the more extreme target levels (i.e., when switching from dark to bright or vice versa).
Here is another observation regarding the pixel reset pulse. Although we cannot measure the pulse width and amplitude on a single-pixel level directly, we still can infer the relative pulse energy from our bandwidth-limited measurements – at least for the settled portion of the pixel response curves –, namely by comparing two simple measures: the average luminance (LP) over the entire refresh cycle (i.e., including the pulse) and the average luminance (L0) over the refresh cycle excluding the pulse. The relative reset pulse energy e is then simply defined as e = 1 - LP / L0. If, on a single-pixel level, the pulse level is always zero and the pulse duration is constant (i.e., independent of the pixel level), then we would expect the relative pulse energy to be the same for all pixel levels. This, however, is not at all what has been measured – see Figure 8. Although the relative pulse energy scales nicely with the refresh rate, which is in line with the reasonable assumption that the pulse duration does not depend on the refresh rate, the relative pulse energy strongly depends on the luminance level. Mind you, this is just for refresh cycles where the pixel value remained unchanged; it is not for refresh cycles that involve an actual change in the pixel value. This is why we cannot draw any conclusions from this finding other than that the luminance settling behavior might be more affected by the reset pulse than expected – in whichever way. There is one caveat: inferring the pulse energy from a bandwidth-limited signal assumes that the measurement system is sufficiently linear. However, given that the ASUS and the MSI, which are two monitors with rather different OLED panels, appear to have such similar pulse energy signatures raises doubts regarding the validity of these measurements. Maybe these results just reflect some shortcomings of the measurement devices (photodiode, amplifier, oscilloscope) and/or the analysis method.
Back to the luminance error pattern. The luminance error, as a however defined measure, might largely depend on where exactly the refresh cycle is considered to start and how the effects of the signal bandwidth limitations are taken into account. There are a number of reasonable definitions for this error measure, and which one is the most appropriate might also depend on the use case one has in mind. One might be better for capturing luminance artifacts (e.g., of moved edges), another one might be better for capturing color distortions. For example, the start of the refresh cycle could be determined for each FROM-TO level transitions individually by aligning it with the 50%-point of the respective luminance transition edge, in contrast to using one absolute time point for all FROM-TO level transitions, which meets a certain criterion, like the 50%-point, only on average. Or, as another example, the pixel reset pulse could be either excluded from the luminance averages or not? Here, we chose to exclude the pulse, assuming that its impact is – if not negligible – at least the same for all level transitions. However, the findings summarized in Figure 8 suggest that both of these assumptions are likely wrong. Neither is the impact necessarily small (see dark levels), nor is the impact the same across different levels.
In conclusion, the results presented in this section should be interpreted with caution.
Color spectra